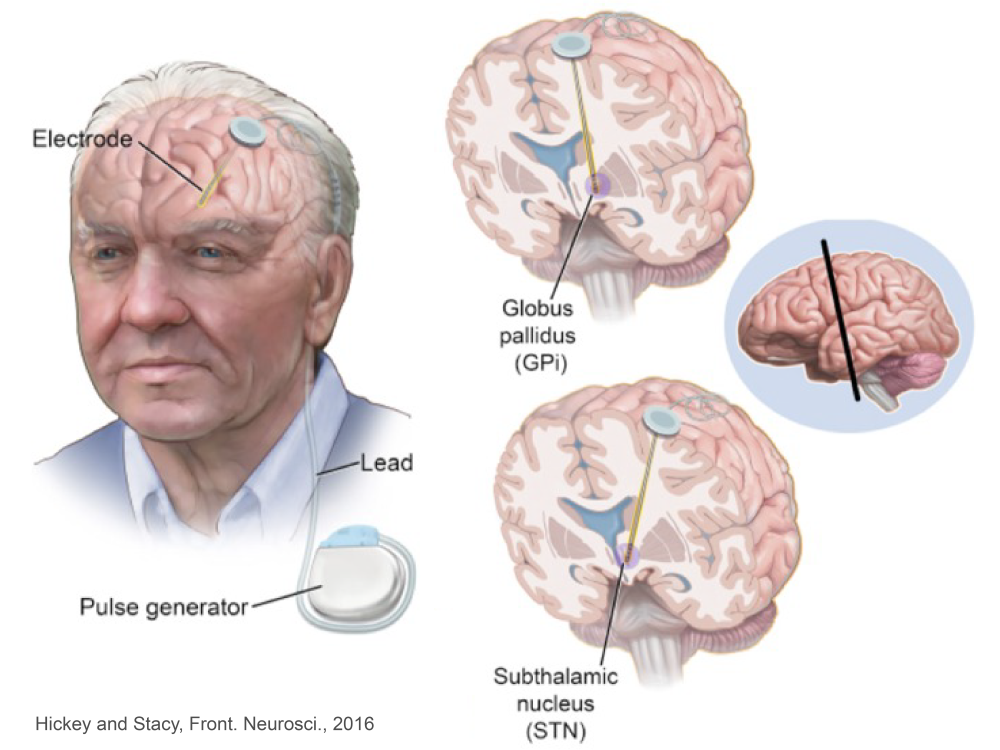
Deep brain stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment that involves implanting electrodes into specific areas of the brain. It is a highly effective therapy for neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. By consistently delivering electrical impulses to targeted regions through a stimulation device implanted in the chest, DBS can help alleviate symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with movement. DBS is adjustable and reversible, allowing for therapy that can be fine-tuned to meet the patient's needs over time.

DBS for non-motor symptoms
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is traditionally used to manage motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease, but patients also experience changes in their cognition and affective processing, which can substantially impact their quality of life. Unfortunately, treatment options for these non-motor symptoms are very limited. However, we recently discovered that altering the frequency of stimulation in the targeted deep brain region, the subthalamic nucleus, can enhance patients’ working memory, which is often affected in Parkinson’s disease. We are now exploring a wide range of possible neuromodulation therapies to address these non-motor symptoms.
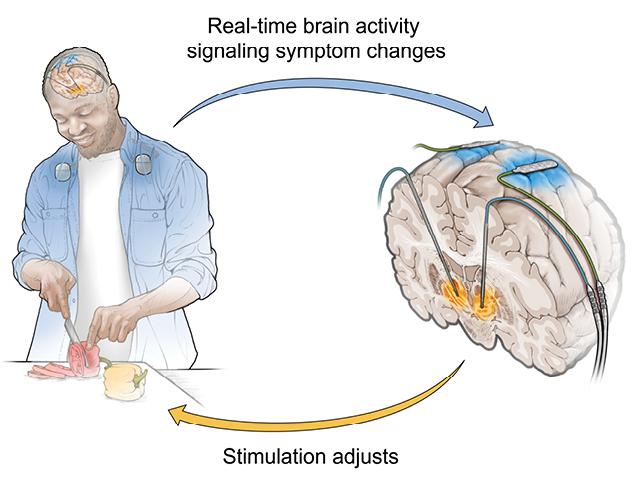
Adaptive deep brain stimulation
Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) is an advanced therapy that dynamically adjusts the level of stimulation in response to real-time brain activity. Unlike traditional DBS, which delivers constant stimulation, aDBS monitors the patient’s brain signals and modifies the stimulation to better match current needs, enhancing treatment effectiveness. We recently demonstrated that this approach can reduce motor symptoms by half and improve quality of life of our patients. Our next goal is to develop responsive algorithms for non-motor symptoms, such as working memory and mood changes. We aim to create a holistic and personalized treatment approach that addresses the wide range of symptoms affecting patients.